An analysis of a central and decentralized solar domestic hot water system for an apartment building shows that the usable solar gain and year-round efficiency are similar, but the solar coverage and the need for backup heat source energy are fundamentally different.
Archiv článků od 1.11.2021 do 16.1.2023
Recently, there have been more and more cases of suspected influence on water levels. There are more and more related disputes with this trend. However, the employees of water authorities have no choice but to rely on the experience of the geologist who prepared the project. In terms of form, the project can be processed well. But fatal problems can arise in terms of well operation. A special chapter is the wells for heat pumps with all their shortcomings and huge technical problems with grouting cement mixtures resulting from small diameters of wells. The aim of this paper is to inform about the wide possibilities of well logging to find out the real cause of the problems related to the level drops and to suggest the optimal way of remediation.
Tracer tests (indicative or indicator tests, use of markers) are a key technique for determining preferential flow paths and delineating watersheds in karst. They are also widely used to verify flow and determine transport characteristics at contaminated sites. They consist of injecting a known amount of tracer into a sinkhole or well and taking water samples at the locations where tracer is expected to reappear. Tracer tests make it possible to determine not only the flow velocity, but also the volume of mobile water between objects when discharge is measured, and also how many % of the tracer has arrived at the monitored objects, and thus also how many % of the tracer, on the other hand, is heading to unmonitored/unknown places. In the Czech Republic, tracer tests were so far usually carried out mainly with NaCl, especially in connection with water supply facilities. In the USA and neighboring European countries, the most commonly used tracer for decades has been the sodium salt of fluorescein (hereinafter Na-fluorescein) and other fluorescent tracers, as their background concentrations in nature are mostly zero and modern fluorimeters enable to detect tracer concentrations usually in tenths of μg/l, which allows the injection of a very small amount of tracer compared to NaCl, well below visibility with the naked eye. Na-fluorescein is conservative, well soluble, non-toxic. Analysis consists of either direct measurement of fluorescence with field fluorimeters or sampling and laboratory analysis on a laboratory fluorimeter. A tracer test with Na-fluorescein in 2021 demonstrated the rapid flow of water from the Bubovický stream sink in the Český Kras to the springs in Sv. Jan pod Skalou and the surrounding area, and on the contrary refuted the possibility that the water from the sink is connected with the water supply well in Srbsko. The tracer test with Na-fluorescein carried out in 2022 in the Chýnov cave aimed to more accurately characterize the connection of the underground flow with the spring Rutice – drinking water supply for Chýnov town. A positive statement was obtained from the regional public health authorities to carry out the above-mentioned tracer tests. Tracer tests with Na-fluorescein can now be used in the Czech Republic in the same way as in neighboring countries. In conclusion, it can be stated that tracer tests are an effective tool for monitoring groundwater flow not only in karst environments. They can be used to confirm or disprove the rapid connection of sinks, streams, and other objects with drinking water supplies, thereby targeting measures to prevent the possible contamination.
The global pandemic that has swept the world in the last two years has affected most of the population. However, the pandemic has also had an indirect effect on water resources in the water sector. One such example is the almost borderline depletion of groundwater reserves at the Koberovy site, Jablonec nad Nisou district.
The area of interest is interesting from a geological and hydrogeological point of view only because it is located on the border of the Podkrkonoše and Bohemian Cretaceous basins. It is an area with a small catchment area, lower rainfall and also higher groundwater abstractions, i.e. an ideal location for the problem that came at the turn of 2020 and 2021.
In the Koberovy community, groundwater withdrawals from the water supply pumping facility, the drilled well KH-3, increased threefold over the area‘s groundwater table during this period. This has created a significant problem affecting groundwater management in the area. Thanks to the established system of express pumping tests at the intake facilities managed by Severočeské vodovody a kanalizací, a.s. (referred to as SčVK) and field investigations at the site, causes have been identified and solutions proposed that are not ideal from the point of view of the water supply hydrogeologist. As a result, the hydrogeologist recommended adjusting the pumping regime, which was to „buy time“ until the necessary change in the concept of supplying, the area of interest, with drinking water.
The increasing incidence of “legionnaire's disease” caused by strains of Legionella pneumophila bacteria indicates an underestimation of the risk not only on the side of hot water production, but above all in its distribution through internal water supply. And what the public does not expect at all, even when distributing cold drinking water.
Tritium (3H), radioactive hydrogen, which occurs on the Earth's surface in low concentrations, can be used as a tracer due to its suitable properties. For this purpose, tritium was monitored in groundwater and precipitation samples. The tritium concentration in groundwater was lower than in precipitation. This is caused by the radioactive decay of tritium, infiltrated from the surface into groundwater, where the connection with the surface is limited. Tritium concentration can therefore be used to infer the rate of connection between groundwater and the surface and can be used to estimate the level of infiltration or the vulnerability of groundwater.
In the Brno area there are abundant groundwater sources in artesian structures. The hydrogeological aquifer of artesian water are Miocene sands covered with the position of Baden's calcareous clays. Under the Brno there is therefore a usable hydrogeological structure, able to serve as an alternative source of water to bridge emergencies and crisis situations. The expected usable reserves of artesian water are 200 to 300 l.s−1. The yield of the structure may be threatened by excessive water extraction, as artesian waters have been (and in some cases still are) used mainly as a source of water for industrial enterprises. In 2021, the first stage of hydrogeological work took place, the aim of which was to revise selected existing hydrogeological wells, which could be used as potential sources of drinking water to ensure the required volumes of water for the needs of emergency water supply of Brno city. In 2022, the second stage of work took place, the aim of which was to define land suitable for excavating new wells.
Design engineering using standard objects brings new possibilities to water management design practice. Similar to CAD tools in the past, integrated engineering now represents the gateway to the world of digitization of water management units and can be understood as an effective pre-step before the introduction of BIM, enabling the creation of digital twins and operational optimization. These new procedures can open the gates of perception of the project and management of the whole in hitherto unknown levels. Due to emerging legislative and business trends in the Czech Republic, we can expect an increased demand for digitally processed projects in object architecture, enabling an interconnected approach to the creation and management of documentation in individual phases of the life cycle of a technological unit.
The article shows the ways of using load profiles of hot water heaters defined by Commission Regulations No 811, 812, 813 and 814/2013 to construct a cumulative hot water consumption curves. The authors point out errors commonly made by designers of hot water preparation systems in relation to the use of the load profiles. The conclusion of the article contains a comparison between consumption curves obtained with use of the hot water heaters’ load profiles and real measurements in different types of buildings.
The paper deals with the methods of checking the performed sealing works in its second part. Measurements of the permeability of the grouted environment in the field are evaluated, the findings of the grouting records are analyzed and the cement content in the taken samples of the grouted soil was determined in laboratory conditions. Finally, the recommendations for remediation are summarized.
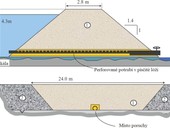
The ever-recurring high levels of the river Danube have forced Bratislava to be protected from floods. In the western part of the city, it was necessary to ensure the sealing of the heterogeneous fills located just on the banks of the Danube. The performed sealing works did not take into account the actual properties of the subsoil. The first part of the paper deals with the factual situation at the site and the shortcomings of subsoil injection.
Thermal baths in Slovakia are producers of wastewater, which have considerable enegry potential. Wastewater often exceeds the maximum temperature that can be discharged to the recipient without harming the environment. In many cases, this requirement is not met, and swimming pool operators must face sanctions for environmental pollution. The aim of the paper is to present the possibilities of using the energy potential of wastewater, which would ensure its required temperature.
The current way in drainage of roads is the concentration of rainwater in the subsoil of roads, so that rainwater does not drain into the sewer system, but freely infiltrates into the subsoil. The aim of this research is to optimize the structural layers of green parking lots with AS-TTE grassing blocks. During the design of structural layers and new types of materials, will be optimized to allow maximum water infiltration into the subsoil and at the same time keep the requirements for load-bearing capacity of structural layers according to ČSN 72 1006. Laboratory tests will be performed focusing on basic physical and mechanical properties, water permeability and adsorption of oil drips.
This paper introduces the results of the project „Tools for effective and safe management of rainwater in Prague city – RainPRAGUE”. Achieved results show the options for higher living standards for inhabitants in urbanised area of Prague city regarding to current and expected trends in climatic change. The project consists of three concepts. The concept 1 was focused on effective management of rainwaters in the urban area of Prague vicinity. Concept 2 was focused on WEB-GIS-based software that will be used to manage emergency hydrological situations on watercourses within the area of Prague city. It will help to prevent and protect the resident population, property and the environment against negative impacts of flash floods. Concept 3 was aimed to develop of WEB-GIS-based software that can assist in delineation of areas with heightened risk of surface runoff, erosion and sediment/pollutant as well as undue drainage runoff. The WEB-GIS is located on the following link (https://rainprague.vumop.cz/).
One of the causes of earth fill dam failure are internal erosion. To simulate these phenomena, a number of software are available to calculate the failure of an earth fill dams due to overtopping or due to internal erosion. For this purpose, software (SW) A Rapid Embankment Breach Analysis (AREBA) was chosen, for which a one-way sensitivity analysis was performed. The paper aims to understand the key geotechnical parameters input to the SW AREBA and their influence on the dam breach hydrogram, the size of the breach and also on the time characteristics. The most sensitive parameters influencing the outputs are the Manning´s roughness coefficient and the erodibility coefficient. These two parameters should be varied by the Monte-Carlo method in the AREBA.
Reducing the consumption of non-renewable raw materials has become a growing issue in recent years. The construction of constructed treatment wetlands generates a significant consumption of natural aggregates, which can be classified as non-renewable raw materials. For this reason, it is necessary to try to find alternative materials to natural aggregates. A substitute for conventional aggregates may be recycled construction materials, which are still not as widely used as natural materials, mainly due to their low quality. The currently available materials should be evaluated in terms of replacing the main filter material of vertical filters, as this is where the consumption of natural aggregates is highest. The aim is to ensure financial savings by using more affordable recyclates, but also to preserve sufficient natural resources for future generations.
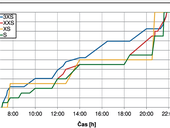
The article provides findings from research on the duration of peak flow in an apartment building at all measurement days. The first part of the article describes the measurement of flows in an apartment building. Second part of the article describes an evaluation of the measured data in individual days in the apartment building. The third part of the article will discuss the evaluated results and a brings a summary by the author.
The aim of the article is to describe the main indicators that affect the amount of oxygen in wastewater and its overall quality. There are three environments that characterize wastewater according to the amount of oxygen. After using all the oxygen from the wastewater, negative phenomena often occur. For example, damage to the cement part of sewers, the formation of excessive odors in the environment or the negative impact of wastewater treatment. The article also includes measured values of the oxidation-reduction potential in a real pumping station in a combined sewer.
The use of SARS-CoV-2 RNA as a biomarker of COVID-19 in wastewater appears to be an appropriate tools for the establishment an early warning system for successful monitoring of infectious outbreaks before an epidemic occurs. SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA fragments are secreted by infected individuals in wastewater excrement, where they can be detected by the quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) method. Within the project “Utilization of wastewater monitoring as an early warning tool against the emergence of an epidemiological situation” in 2021, wastewater sampling methods were optimized with subsequent verification of these methods on wastewater samples taken in subsequent waves of the epidemic.
zpět na aktuální články